Would you like to surf the Web without being tracked? With today’s internet becoming a “wild west,” it is imperative to protect yourself from being monitored by the multitude of players such as marketers, government agencies, advertisers and website owners.
The inherent dangers that lurk every time you go online including malicious links and outright attacks by hackers call for diligence in covering your tracks at every turn on the web.
Surfing the internet today is like walking on the street. If someone were to follow you, they are more likely to know which places you visited, what you touched, the people you talk to and almost everything you do.
On the internet there are many motives why individuals and companies would be interested to know what you are up to.
Governments spy on citizens for various reasons including:
- To stop criminals or terrorists
- General intelligence gathering
- To suppress dissent (in cases of oppressive regimes)
Marketers on the other hand need information about you mainly for targeted advertising.
Hackers will find ways of infiltrating systems to steal such information for malicious purposes.
If appropriate measures are not put in place, browsing the web becomes a massive wilderness where hackers roam unhindered and companies and other individuals harvest your personal information for their own benefit.
Every time you go online there are little traces that you leave behind without your knowledge which can be used to identify you and your activity during that period.
The websites you visit have embedded technology that enables them to identify:
- Your IP address – which identifies the device you are using
- Your location
- Operating system
- Browser you’re using
- The pages you visit
These and many other parameters are used to profile your behavior while online. Cookies for example, are responsible for the activity of collecting data. These are small pieces of data sent from a website and stored on your web browser, indicating your browsing pattern. This data is useful since it is used by companies to display ads that are relevant to you based on your online history.
There are various ways you can hide from all these prying eyes. How you access the web, which places you visit and what you do when you are online determines how safe you are and the level of anonymity you will be able to achieve.
Why you should be anonymous while online
Browsing the web without leaving a trace helps you to protect your privacy. Whether you are hiding from a repressive regime, negotiating a business contract or conducting a financial transaction with your bank, the need to ensure that nobody is peeping at the information you are sending or receiving is very important.
When you are anonymous, you protect yourself from
- Hackers – they are always on the lookout for any vulnerability in your online activities to steal your personal data. They can use your IP address, browser cache and cookies to find out your location, what kind of computer or browser you’re using, which websites you have visited what information you enter into those sites.
This can allow the hackers to easily gain entry into your system and steal your passwords and other sensitive information.
- Advertisers – when you search for information online, websites use cookies to track the search keywords used, your IP address, the pages you visit and many other characteristics.
This helps the advertisers to customize which ads you see based on your browsing habits.
Remember free resources come at a price. When you visit websites or search Google you may get what is considered as free information. To maintain these resources, the owners largely depend on advertisers.
To find premium advertisers, these websites must demonstrate value by touting how much they know about you – the visitor.
- Marketers – some websites will require you to enter your email address to access their content. Your details may be sold to marketers leaving you with thousands of spam emails in your inbox.
- Oppressive regimes – some governments censor the kind of content citizens are allowed to access. Browsing anonymously prevents such regimes from keeping track of your online activities.
Anonymity can also help you to access content that has been blocked based on your geographical location. In this case you may want to trick the website into thinking that your request is coming from a different location based on the IP address you are using.
The following are measures you can put in place to remain anonymous online:
1. Browsers And How To Tweak Them For Privacy
There are many applications on smartphones, desktops and other devices that connect directly to the internet. However, your browser remains the primary way in which you connect to web resources. You can tweak around any browser to enable you hide your activities online. Most browsers have in-built security tools that can be used to your advantage.
Before we delve into the the different ways of making browsers safe for your anonymity, the following guidelines are important to note.
- Regularly update your browser software to guarantee your anonymity. these updates contain important improvements to counter any vulnerabilities hackers may have discovered.
- Avoid installing browser extensions, plug-ins, add-ons and toolbars which pose security threats depending on what kind of information they collect.
- Disable pop-ups on your browser. Some pop-ups can be used to launch malicious programs on your devices.
- For the browser extensions, plug-ins, add-ons and toolbars that you really need and are already installed, always enable automatic updates to avoid vulnerabilities usually exploited by hackers.
- Check your browser’s preferences and security settings to determine whether they protect your privacy.
(a) Private browsing
The commonest way to cover your tracks online is to use private tabs in your browser. Private browsing is a useful feature in most web browsers that is used to disable the cache and browsing history.
This helps you to browse without your searches and history being stored for later retrieval. This privacy protection is only within the browser and does not extend the protection to other applications you may be using. Traces of your online activity may be retained on your device’s memory or on websites you have visited.
Private browsing is useful in several situations;
- It prevents you from accidentally saving login information which is important to safeguard your important credentials such as bank details.
- It prevents anyone from finding out your online activities by looking in your search history.
- It helps you find fresh and specific information which is not influenced by your previous browsing history.
To use private browsing in your browser, follow the guidelines below.
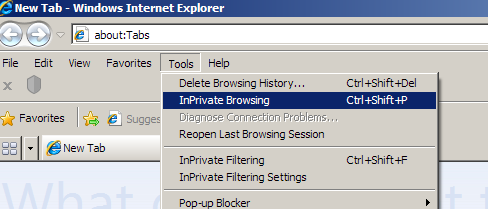
In Chrome – Click on the Chrome menu button (⋮) and then click on “ New incognito window” to browse in “incognito” mode.
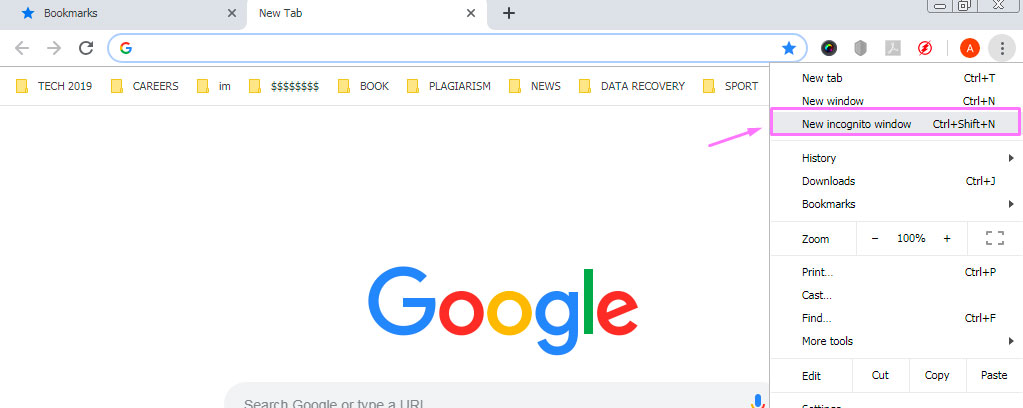
In Opera – Click on Menu (the Opera logo in the left top corner). Click on “New private window” to start using “Private browsing” mode.
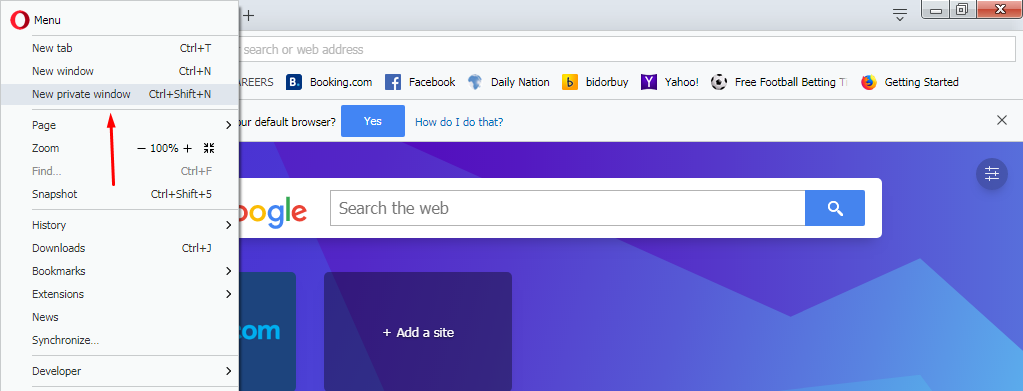
In Microsoft Internet Explorer – Click on “Tools” on the menu bar and then “InPrivate browsing” to start browsing anonymously.
In Mozilla Firefox – click on the “File” menu item and then click “New private window” to start using the “private browsing” mode.
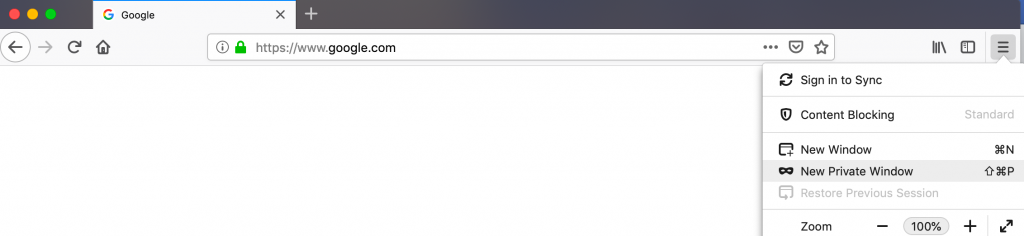
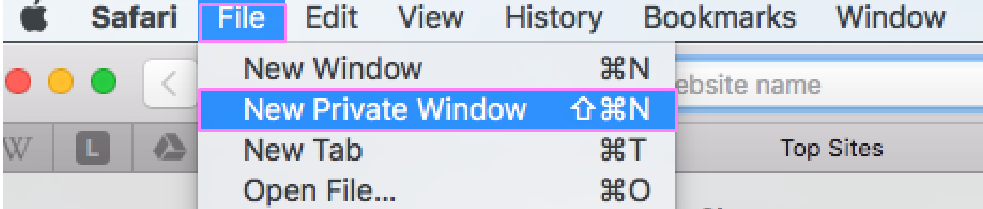
In Apple’s Safari – Click on the “File” menu item and click on “New Private Window” on the drop down menu that appears. You can also hold down the Command+Shift+N keys to open the private window.
In iOS Safari – Tap the Pages button on Safari’s menu at the top right corner. When the window opens tap on “Private.”
b) Private Searching
You can also use other search engines which do not track your searches. Examples include;
- DuckDuckGo – unlike the most popular search engines such as Google, Bing or Yahoo, this search service does not save your searches nor build a profile based your activities online. This means that you cannot be targeted by advertisers since DuckDuckGo does not capture your data.
- Ixquick – also known as Startpage, this search engine provides search results from over ten search engines in full privacy. It does not record users’ IP addresses or make a record of their searches. Actually the engine’s privacy practices have earned it top rating from the European certifying authority – EuroPriSe.
Note: The big search engines use your searches and browsing history to speed up your browser by predicting the sites you are likely to visit. This also helps them to tailor the ads that are displayed for you based on your location and preferences.
(c) HTTPS Everywhere
When you access a website, the use of https before the web address ensures that your communication with that site is secured. An HTTPS means that the data being send and received is encrypted. This protects information such as passwords and account information from falling in the wrong hands.
The “s” in https stands for “secure.” This is confirmed by the presence of a padlock in the address bar (see below, left side).
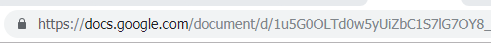
Now, if the website you are visiting does not show https, you can force it to connect securely. This is done using the HTTPS Everywhere feature which can be installed on your browser or you can type https before each url every time you want to connect to a given resource. This automatically enables an HTTPS encrypted connection for any website that supports it.
You can easily achieve this by installing the HTTPS extension which is available for Firefox, Chrome and Opera browsers. It’s also available for Firefox on Android.
This extension is produced by the Electronic Frontier Foundation and can be found here.
Not all websites support HTTPS Everywhere and in such cases you may have to find another way to be secure.
(d) Disabling Cookies in your browser
As mentioned, cookies store information about the web pages you have visited on your browser. You can disable these cookies to prevent them from storing your data.
Caution: cookies have become so important in today’s ad-oriented web. Many websites depend on cookies to profile their visitors and to attract advertisers.
Most of the websites today will inform visitors that their pages use cookies and will require you to accept them. A majority of them will disable a lot of their services if you disable cookies. Some won’t even let you visit them unless you enable cookies.
The same applies for some apps which may contain an option to block cookies, but in turn will disable the website you are using.
To disable cookies in the major browsers, follow the instructions below:
Google Chrome (desktop)
1. Find the menu button (⋮) on the in the upper-right corner of the Chrome window and click on it.
2. Click on “Settings” then “Advanced” tab or “Show advanced settings.”
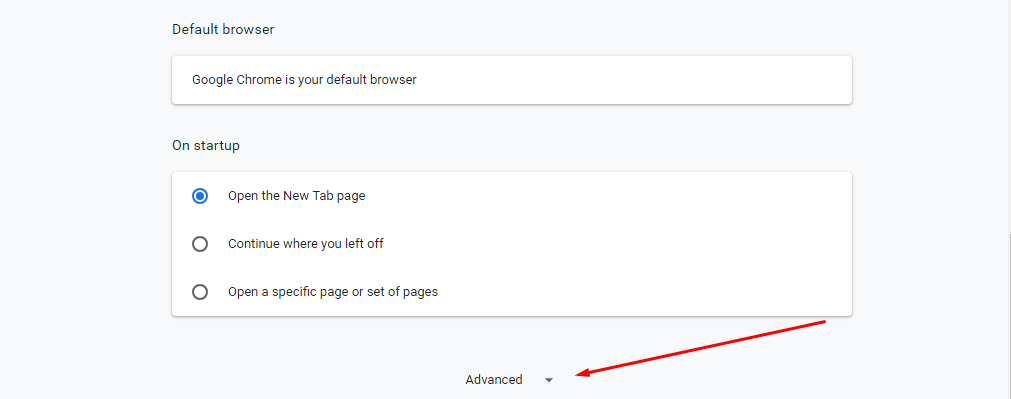
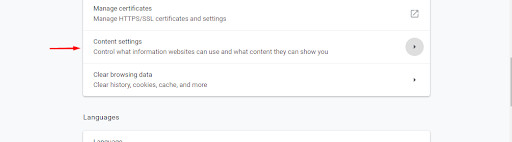
3. Find the “Privacy and security” section. Next Click on “Site Settings” or “Content settings.”
4. Click on “Allow sites to save and read cookie data” slider to disable cookies. Enable the “Block third-party cookies” box.
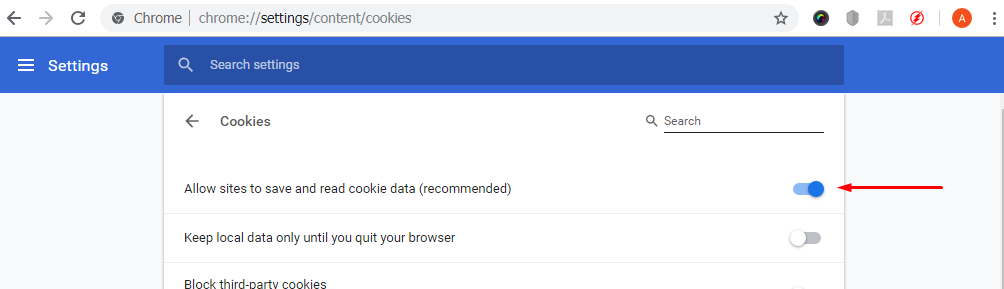
If you are using an older version of Chrome select “Block sites from setting any data.”
Remember one of the ways to deal with emerging threats is to update your browser.
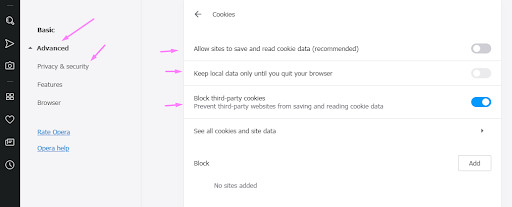
Google Chrome (on Android)
Tap the Chrome menu button (⋮).
Tap Settings > Site settings
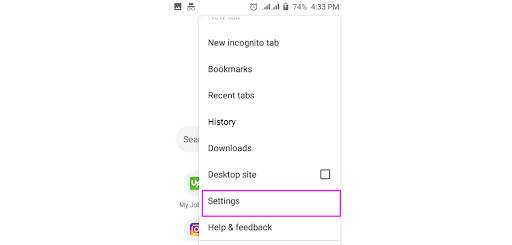
Tap on “Cookies”
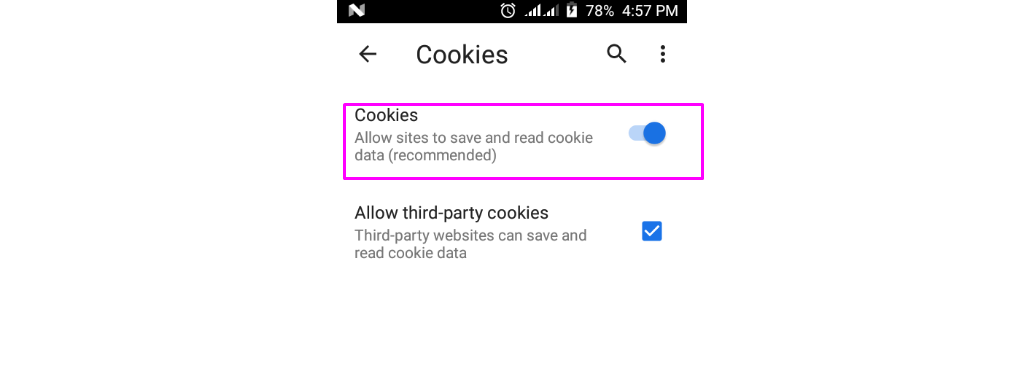
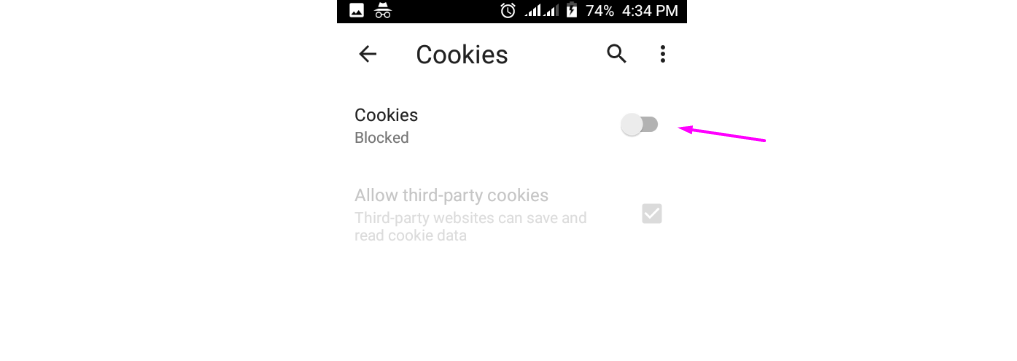
Toggle the Cookies slider to “Blocked”
Mozilla Firefox
Follow the sequence below for Firefox:
Find the Firefox menu button in the upper-right corner of the window and click on it. on the drop-down menu click on “Options.”
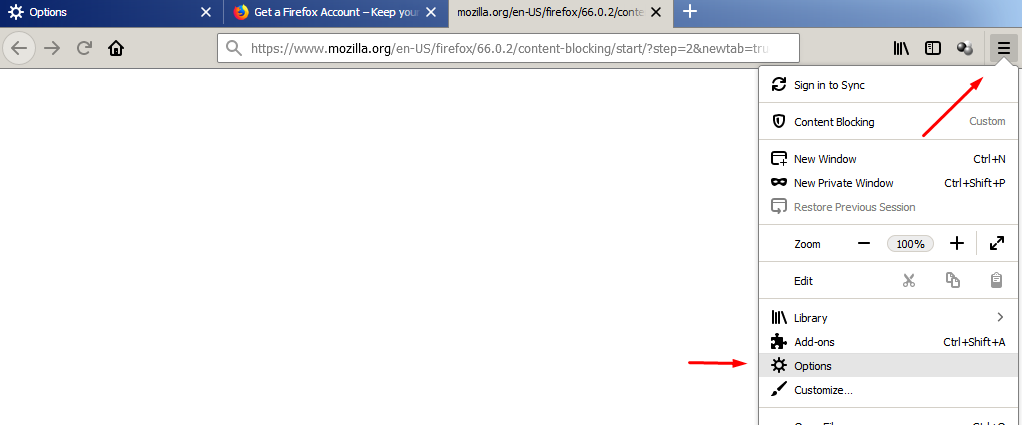
Click on the “Privacy and security” section. Under “Content Blocking,” choose “Strict” to block all trackers and cookies.
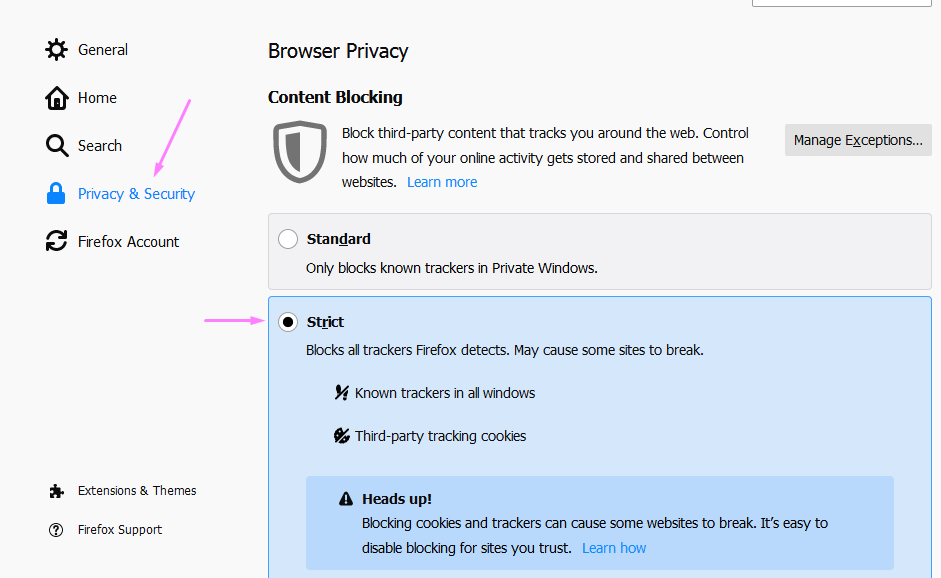
Under “Send websites a “Do Not Track” signal that you don’t want to be tracked” choose “Always.” Under “Cookies and Site Data,” enable “Delete cookies and site data when Firefox is closed.”
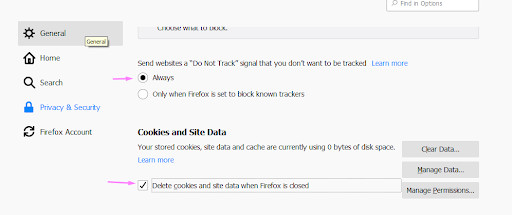
Opera
Use the guidelines below for Opera
- Click on Menu (the Opera logo in the left top corner). Click on Settings>Advanced>Privacy and Security>Content settings>Cookies.
- Deselect “Allow sites to save and read cookie data.”
- Deselect Keep local data only until you quit your browser
- Select “Block third-party cookies.”
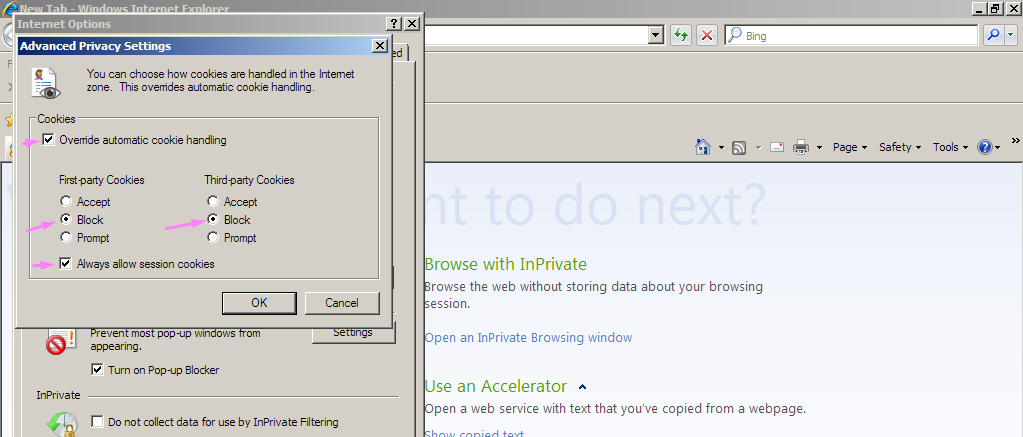
Microsoft Internet Explorer
- Click on the Tools menu or the Gear button. If the two are not visible simply press ALT on your keyboard.
- Click on Internet Options followed by the Privacy Tab.
- Click the Advanced button
- Click Block for First-party cookies and Third-party cookies
- Click the Always allow session cookies box.
- Click OK to save your changes. Internet Explorer will no longer save cookies.
Microsoft Edge
Microsoft’s Edge, which was released in 2015, is the latest browser meant to replace Internet Explorer. For devices running Microsoft’s latest OS, Windows 10, Edge is packaged as the default browser.
To disable cookies in Edge, use the guidelines below:
- Click on the menu button( …) at the top right corner.
- Click on Settings from the drop-down menu
- On the Advanced settings section, click on “View advanced settings.”
- Click on the “Cookies” drop-down menu and choose “Block cookies.”
Safari on desktop
- On the menu, click the Safari menu item which appears in the menu bar when a Safari window is open.
- Click on “Preferences” then on the “Privacy” tab.
- Under Cookies and website data, click the “Always block” radio button.
Safari on iOS
- Tap the Settings app
- Tap on Safari
- Under “PRIVACY AND SECURITY” tap on “Block cookies”
- Tap “Always block” for cookies and website data. The app will will no longer save cookies on any of the websites you visit.
(e) Clearing your browser’s cookies
Clearing your browser’s cookies ensures that anybody looking at your device will not be able to see your search history, the resources you accessed and any autofill information used in your online sessions.
Firefox
Find the Firefox menu button in the upper-right corner of the window and click on it. On the drop-down menu click on “Options.”
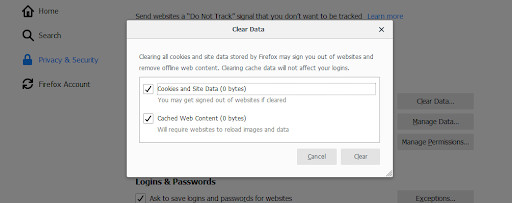
Click on the “Privacy and security” section. Under “Cookies and Site Data,” click on “Clear Data.” This will clear all cookies and cached web content.
Opera
- Click on Opera menu>history>clear browsing data.
- Choose the time range, check the boxes for “browsing history,” “cookies and other site data” and “cached images and files.” Click on “Clear data.”
Chrome
- Hold Ctrl+H or find the menu button (⋮) in the upper-right corner of the Chrome window and click on it. Next click on “History” to open the history window.
- Choose “Clear browsing data.”
- Choose the time range, check the boxes for “browsing history,” “cookies and other site data” and “cached images and files” and any other items you want to disappear.
- Click on “Clear data.”
Internet Explorer
- Hold Ctrl+H or find the menu button (⋮) in the upper-right corner of the Chrome window and click on it. Next click on “History” to open the history window.
- Choose “Clear browsing data.”
- Choose the time range, check the boxes for “browsing history,” “cookies and other site data” and “cached images and files” and any other items you want to disappear.
- Click on “Clear data.”
(f) Plugins
Plugins are another alternative that can be used within a browser to improve internet safety and privacy. A plugin is a software component that adds specific functionality to an existing computer program. This means that when the plugin is installed it ates the possibility of that program being customized to execute a function that was previously unavailable through the stand-alone program.
For example, a plugin such as Ghostery works to to keep you safe and secure while you’re browsing by preventing anyone from stealing your data or tracking you.
Plugin are easy to install and use. They provide superb protection and can be removed with ease if you no longer need them.
Anonymous browsers – Tor
Tor is a very interesting browser which allows you to go online in a completely anonymous way.
The Tor browser makes use of a network of volunteer servers around the world to encrypt your connection and protect your data from being seen by anyone. This happens through Tor (“The Onion Router”) – a network of virtual tunnels run by volunteers all around the world.
Tor will give you a very good level of anonymity for you to browse the web without being tracked. It is a free, open-source software that is available for download.
The Tor network anonymizes your web browsing by encrypting your connection then bouncing it around the internet through a series of relays scattered worldwide. With more than seven thousand relays, this network can conceal a user’s location and any activity from anyone conducting network surveillance.
It makes it very difficult to trace Internet activity such as instant messages, location, online posts or sites visited to a particular user.
This is the browser of choice for most people who live in jurisdictions with strict controls on internet access. Journalists in such areas have used it effectively to relay stories that are sensitive.
Although Tor is primarily designed to protect the privacy of users by keeping their Internet activities from being monitored, it does not prevent an online service from determining when it is being used. A website you are accessing can therefore determine that you are using Tor.
To use Tor, you will need to download the application and install it on your computer then run it.
Every time you need to browse anonymously, start the browser and wait for it to connect to the Tor network.
After connecting you can now use it to browse normally but anonymously.
Important notes:
- Although Tor gives you the freedom and ability to conduct confidential communication it does not prevent an online service from determining that you are using Tor.
- Some websites restrict the use of Tor.
- Using Tor will ensure all your connections are secure. If you are using other browsers, utilise the “HTTPS Everywhere” extensions (see details above).
How to stay anonymous when Using Public wifi hotspots
Public wifi hotspots are common in major towns. They are a convenient way to access the internet anywhere. This convenience means that a lot of people connect to these networks giving hackers a diverse group of people to target.
It is important to only use secure networks whenever possible. It always seems very attractive to connect to these networks in public places like coffee shops and airports.
These networks have very weak protocols and hackers take advantage of this to exploit any vulnerabilities in them to attack unsuspecting users.
Some hackers create fake networks that mimic your favorite public hotspot and trick you to connect. When you connect to such a network, which is fully controlled by the hacker, your activities are monitored and your personal data is easily stolen.
Avoid public wifi hotspots at all costs. Only use these networks if you have a secure connection such as when you are using a VPN service or connecting through a proxy server. Use your private home network or ensure the network you are using is protected. Otherwise use your wireless service if you are browsing on your mobile or tablet to connect to the internet in order to safeguard your information.
Alternatively, tether to your mobile device’s LTE connection by creating a personal hotspot. Ensure that you secure your personal hotspot with a strong password.
Use of Proxy servers
Proxy servers are anonymous servers that work through web forms so that all your internet requests are first filtered through the form. The server acts as an intermediary for requests from you when you are seeking resources from other servers. For example when you need to access a particular website you send a request to this server and it does it on your behalf enabling you to hide your identity.
An anonymous proxy server ensures your privacy by hiding the public IP address that your internet service provider uses to identify your device and and route traffic through other servers for you to access online resources.
For example, a proxy site can help you access content that has been blocked due to your geographical location. If the website thinks that your request is coming from a supported country, it will allow you to have access. You simply make sure you are using a proxy located in a country that is supported.
If you are on you are on a network that blocks a specific site, but allows a proxy, you can circumvent that by using the proxy to access the blocked site.
Before you select which proxy server to use you need to find out whether it has acceptable speeds. Anonymous proxies normally don’t perform at optimal speeds like your normal connection due to the processing of your traffic through the proxy server.
You may also look around to see previews and identify a reputable brand with a clear privacy policy.
Important Note:
There is a difference between proxy servers and a VPN. A proxy server will handle your traffic which originates from the browser that is using the proxy site while a VPN will handle all traffic originating from your device (whether from your browser or other programs). VPNs are also convenient because they are able to connect your device automatically on startup while proxy sites will need a prompt through your browser.
Web based proxies
Web-based proxies are easy to use because you do not need to configure anything. You simply use the internet in the normal way but through the proxy website.
Examples of free web-based proxy servers include Anonymouse, Hidester, Hide.me, ProxySite.com, KProxy and many others.
To use a web-based proxy servers, search for the server on Google or simply search for “free web based proxy servers” and choose one.
Go to the server’s site and type in the web address of the resource you are looking for (You are basically using the proxy’s search bar). The proxy server will connect on your behalf and retrieve the pages ensuring that the IP address and any other information the remote server identifies are those of the proxy, not yours.
Free proxy servers may display ads on top of your browser. This helps to keep the services free.
Browser based proxies
For browser-based proxies you need to configure the address of the proxy server in the web browser.
For Chrome
- Click the Chrome menu (⋮) in the top-right side of the Chrome window.
- Click Settings.
- Scroll down and click Advanced.
- Under the “System” heading click on “Open proxy settings.”
- In the “Internet properties” window {or the Network window on Mac} click on “Connections” tab.
- Click on LAN settings under the “Local Area Network (LAN) settings” {or check the “Automatic Proxy Configuration” box if you’re using a Mac}
- In the “Proxy server” heading check the “Use a proxy server for your LAN” box {enter your proxy server’s address in the text box that appears on Mac}
- Enter your proxy server’s information by filling out the proxy server’s address and proxy server’s port number. On the Mac check the “Use Passive FTP Mode (PASV)” box.
- Click OK to save the proxy settings.
- Click “Apply” to effect the changes.
- You may need to restart Chrome to browse anonymously.
Note:The Internet Options settings also apply to Internet Explorer such that the Chrome proxy will also work for Internet Explorer.
For Firefox
- Click the menu button ☰ in the top-right corner of the Firefox window.
- Click on “Options” {or Preferences on a Mac}.
- Click on Advanced.
- Click the Network tab.
- On the right of the “Connection” heading, click Settings.
- below the “Configure Proxies to Access the Internet” heading click the Manual proxy configuration circle.
- Enter the proxy information by filling out the proxy server’s address in “HTTP Proxy” and the server’s port number in “Port.”
- Below the “HTTP Proxy” field, check the “Use this proxy server for all server protocols” box.
- Click OK to save the new settings.
For Internet Explorer
- Click on “Tools” then “Internet options.”
- Click the “Connections” tab.
- Under the “Local Area Network (LAN) settings” heading, click LAN settings.
- Below the “Proxy server” heading, check the “Use a proxy server for your LAN” box.
- Enter your proxy server’s information by filling out the proxy server’s address in the Address bar and the proxy server’s port number in the Port bar.
- Click “Apply” to effect the settings.
- You may need to restart Internet Explorer to start browsing anonymously.
For Microsoft Edge
- Open “Start” by clicking on the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of your screen.
- Click on “Settings” (the gear icon) in the lower-left side of the Start window.
- Click on Network & Internet (the globe-shaped icon).
- In the window that opens, scroll and click the Proxy tab.
- Enable the proxy server by clicking the switch below the “Use a proxy server” heading (if the switch is “On,” the Microsoft Edge proxy is already enabled).
- Enter the proxy server’s information by filling the proxy server’s address in the Address bar and the proxy server’s port number in the “Port” bar.
- Click “Save” to apply the proxy settings to Edge.
- You may need to restart Edge to effect the changes.
Important Notes:
- Anonymous proxies may retain your IP address and other information on their servers and may disclose this data to third parties. They are also capable of retaining session cookies when the your connection unencrypted.
- In some countries, it is a crime to use an open proxy (for example the E.U).
Using a VPN
A VPN is a is a more sophisticated service that you can deploy to help you remain anonymous when you are online. A VPN or virtual private network is a service made up of a network of servers that allows you to change your IP address and encrypt the data you send and receive, giving you both security and anonymity.
When you change your IP address, you basically trick your device to believe that it’s in another location. The Virtual Private Network provider will replace your device’s initial IP address with a different one that will show you are in any of the gateway cities in their network.
Every time you use the VPN service your IP address changes making it difficult for anyone to track you or create a profile that can be used for targeted advertising.
Before you choose a VPN provider ensure that a “no logs policy” is in place. This means that the VPN does not view or store your web traffic. Most free VPN services will tend to sell your data to marketers. A paid service is a better choice for your privacy.
A good VPN service can be very useful if you use public Wi-Fi hotspots which tend to be insecure and are easy targets for hackers. Using a VPN service makes it difficult for someone to hack into your system and access your sensitive data such as e-mails, financial information or passwords.
If you use Opera as your browser it has a built-in VPN that you can enable to browse anonymously.
- Click on the Opera menu and click on “Settings”
- Under Advanced, click on “Privacy and Security”
- Scroll down to VPN
- Toggle the Enable VPN slider to activate the inbuilt VPN service.
Important note; your browser could be storing a history of your searches online even when you are using a VPN service. Refer to the section on “browsers and how to tweak them for privacy.”
Managing how email is used Anonymously
Email has been and remains an ubiquitous tool for communication. If you must use email but are interested in remaining anonymous, there are several ways to achieve this.
Important note: do not enter your email address every time you are asked by the websites you visit. Email is part of your personal information which is highly sought by marketers and hackers alike. However, you may have to give your email to social media sites such as twitter of Facebook which are also an integral part of modern communications.
Use of anonymous email
If it’s important for you to access content on a site that requires an email address, you can create a spam email address and use it to log in. Such an email does not have to contain your real personal information that can be exposed and used maliciously.
(b) Use of an alias email
An alias email is basically tweaking your current email address to create a forwarding address such that when you send mail through the address, the recipient will see your forwarding address, and not your real email.
Your incoming mail (both to your real email and the alias) is forwarded to your regular inbox. This keeps your real email address secret but lets through any spam directed at your alias.
Your regular email can be tweaked to allow you to create an alias.
Gmail
Open your Gmail in your browser and click on on the cog icon in the top right of your inbox window. Click on Settings on the drop-down menu. Select “Accounts and import”>”Add another email address.” Enter your name and email account information. You will be asked to verify the information.
After verifying the new address through your other accounts, you can now change the “from” address in your primary Gmail account. When sending an email, click the “From” line, then select the alias address you want to send your message from.
Yahoo
In Yahoo Mail click on the Settings menu (the cog icon on the right top corner in your inbox). Click on “more settings” and select “Mailboxes,” then click on “Email alias.” Click “Add” and enter your new email address. Click on “Setup” and then enter your account information. Click “Finish” to complete the process.
Outlook
Under “Account settings” click on “Account Aliases” to create upto 10 new accounts.
(d) Use of a Disposable email account
Simply create a new email account with a fake name which you can use for a specified period of time and get rid of it.
Sign up for a disposable email service. This kind of a service creates a temporary forwarding address for a limited period. When this period elapses, the account is deleted. Services such as Mailinator, Airmail and GuerrillaMail.com are free to use for a short while.
You can also create a disposable email account at Yahoo. Follow the process above and click on “Disposable email address” found below “Email alias.”
For most other domains, you will find tools for creating aliases. Have a look around the control panel of your Web Host to see what’s available.
Conclusion
Browsing the web anonymously requires alertness on all fronts. For example, it’s important to log out of all accounts before you start to ensure total privacy.
You can use private searching when you want unbiased search results and simply switch back to normal search for trackers to help you get faster, more convenient results based on what is popular out there. The choices are endless.
Although there is no one solution that can provide complete anonymity online, the different methods we have documented above can be used in combination to provide an effective way to browse the web without worrying about being tracked or losing your valuable data to hackers.